By Ben Reed, Sr. Technical Content Strategist and Sales Engineer
Security breaches have become a weekly occurrence in the news cycle, which has caused businesses to start asking questions. How are they happening? Is my business at risk?
The short answer is yes, your business is at risk. Here’s an overview on how data breaches occur, why they’re on the rise, and what steps to take now to protect your business.
Data breaches can be broken down into three separate categories: IT and business process failures, human error and malicious attacks, according to the Ponemon Institute.
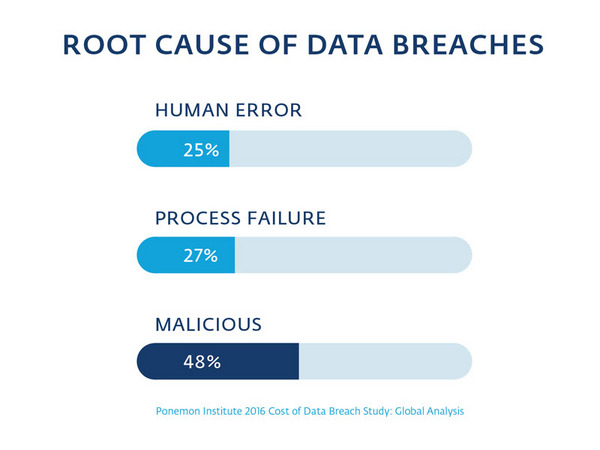
IT and business process failures accounted for 27 percent of the incidents in 2016. These kinds of breaches occur when a company purchases a security solution such as antivirus software or encryption, but doesn’t keep it updated or enforce related security policies over the years. They also occur when a company purchases a security product but never implements it.
Human error, which can include someone leaving a computer unlocked, writing a password on a sticky note, or losing a device, accounted for 25 percent of breaches. Interestingly, 73 percent of devices that were lost or stolen were in the owner’s work area or car.
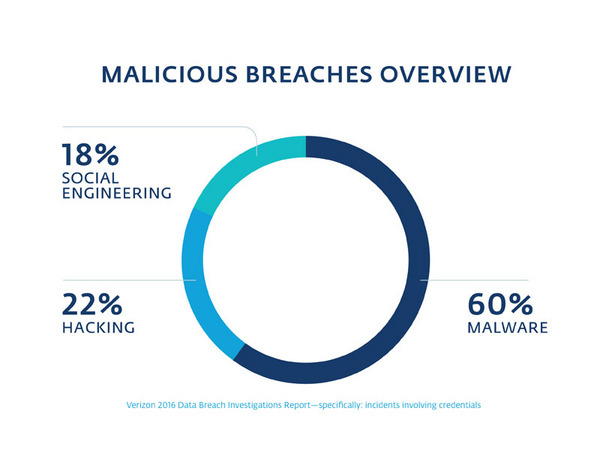
The final category, malicious attacks, is what most people think of when they hear about “hacking” in the news. However, actual hacking is a very small subset of total malicious breaches at just 22 percent. (Most hackers gain access to computers by simply guessing weak or default passwords, or by stealing them.)
The majority (60 percent) of malicious breaches is attributable to malware, such as viruses, with the remaining breaches (18 percent) caused by social engineering.
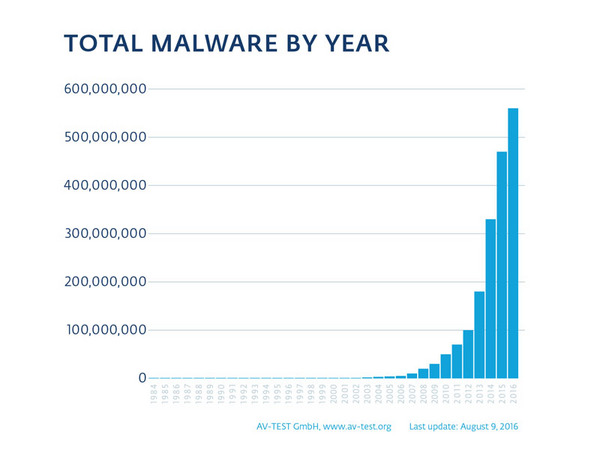
Malware is becoming more of a problem, as the number of malware strains typically doubles every 12 to 16 months. Currently, the independent testing facility AV-Test sees around 390,000 new malicious items per day. Also, malware is no longer Windows specific—it also targets Mac and Linux with programs developed specifically to attack these operating systems. Because Mac and Linux users tend not to have any antivirus protection, when malware is written for these platforms it has a very high penetration and infection rate.
The final type of malicious breach is social engineering, which tends to be a person calling or emailing and pretending to be someone else. The most common form of social engineering is phishing emails. The endgame of these social engineering attempts is to “fish” for information that can be utilized to log into your accounts. Some questions may seem innocuous, such as what is your pet’s name or the street you grew up on, but these are the answers to the most commonly used security questions needed to reset your passwords.
Ask a typical computer user and he or she will claim that they never click on links in email, they never respond to emails from people they do not know, and they always do the right things when it comes to online security. However, the statistics don’t lie: they show that 30 percent of people open phishing emails, and 12 percent of people open attachments. Obviously, more education is required around this topic to protect your company from this ever-growing threat.
So: how to protect your business, computers and data from these different threat vectors? Here are some basics. Overall, your best bet is to implement a multilayered security strategy that can prevent, detect and eradicate threats as well as protecting your data, systems and users.
Malicious Attacks
Implement endpoint security solutions that will protect against viruses, ransomware and other types of malware. For added security and convenience, look for a solution with cross-platform capability that can be easily managed. ESET’s award-winning endpoint threat protection provides comprehensive security that can be managed from a single console with ESET Remote Administrator.
Hacking
Protect against weak or shared passwords with two-factor authentication (2FA).ESET Secure Authentication offers easy-to-implement 2FA, which can protect local desktop logins, remote desktop, VPNs and devices.
Social Engineering
ESET Mail Security ties directly into your exchange server and protects users from phishing schemes and spam emails. Using a cloud provider? ESET Endpoint Security products provide the same level of protection at the email client level, and also feature web access protection to prevent users from visiting potentially harmful websites.
Lost Devices
One of the smartest security moves you can make is to encrypt computers, flash drives and emails so that your data is protected from unauthorized users. DESlock+ Data Encryption will help ensure that your data is inaccessible, even if a flash drive or mobile device is lost or stolen.
IT Issues and Process Failure
What would you do if a natural disaster or power failure crashed your computers? Be sure to have a backup and recovery system in place, such as StorageCraft, that can quickly restore your data, apps and systems. And make sure the security software you choose comes with good customer support. ESET provides free, U.S.-based tech support to help keep you running smoothly 24/7.
With 10 years of IT experience in both small and large organizations, Ben Reed has worked in solutions engineering, system administration and help desk. Ben is an expert in the ESET Remote Administrator and ESET Endpoint Clients, and helps customers with configuration and deployment of ESET solutions.